Why Industrial Operations Depend on AC Hydraulic Power Units
How do industrial AC hydraulic power units differ from DC hydraulic power units?
The main difference between AC and DC hydraulic power units lies in how they’re powered and where they’re used.
AC hydraulic power units run on alternating current, usually three-phase electricity, which gives them the strength and reliability needed for heavy industry. They’re designed for continuous duty, high pressures, and long operating hours, making them the standard choice for factories, steel mills, power plants, and offshore rigs.
DC hydraulic power units run on direct current from batteries, which makes them portable and ideal for mobile equipment. While they don’t match the power of AC units, they shine in flexibility — powering truck lifts, scissor lifts, agricultural machines, and other systems that operate off-grid or on the move.
In short: AC units power industry, DC units power mobility.
What industries rely most on AC hydraulic power units?
Industries that rely on constant, heavy-duty performance—such as manufacturing, energy, marine/offshore, construction, and mining—depend most on AC hydraulic power units. Their ability to deliver continuous power, handle high loads, and operate in demanding environments sets them apart from DC systems.
1. Manufacturing & Metalworking: Factories, steel mills, and foundries use AC HPUs to power presses, stamping machines, injection moulding, rolling mills, and heavy cutting equipment. These processes require steady pressure and long runtimes that only industrial AC systems can deliver.
2. Energy & Power Generation: Hydroelectric plants, wind turbines, and thermal power stations rely on hydraulic power units to operate gates, cooling systems, pitch control, and other critical functions. AC HPUs are favoured for their reliability and ability to run around the clock.
3. Marine & Offshore Oil and Gas: AC HPUs are widely used on offshore drilling rigs, ships, and platforms for winches, steering gear, blowout preventers, and lifting systems. Their robust design and three-phase power compatibility make them dependable in harsh marine environments.
4. Construction & Infrastructure: Large stationary equipment like bridge-lifting systems, tunnel-boring machines, and industrial cranes often use AC HPUs. They provide the high horsepower needed for safe, controlled movement in critical infrastructure projects.
5. Mining & Heavy Equipment: In mining operations, AC HPUs power crushers, conveyors, drilling rigs, and other large equipment that must perform under extreme loads and conditions. Durability and uptime are key, making AC systems the natural choice.
What are the main components of an industrial hydraulic power unit?
This diagram highlights the core elements of a standard industrial AC hydraulic power unit: a motor to drive the pump, a reservoir to hold and cool the fluid, filters and breathers to keep the oil clean, gauges and indicators for monitoring, and relief valves for safety. Together, these parts form a reliable, continuous-duty system capable of powering heavy industrial machinery.
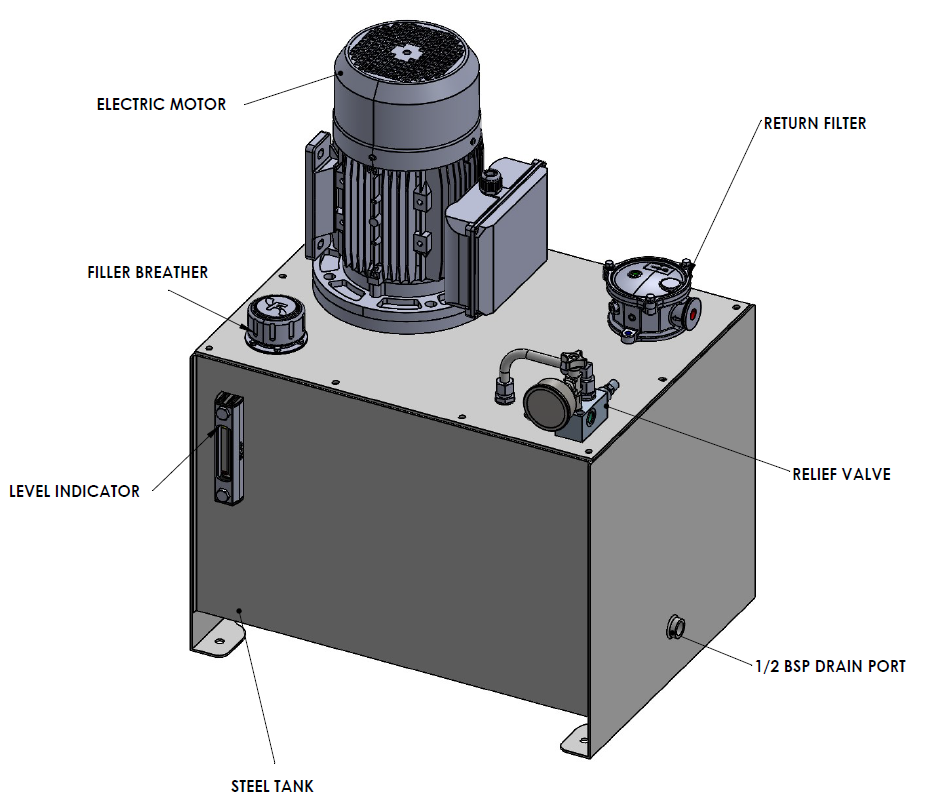
1. Electric Motor: The motor (in this case, IE3 efficiency with PTC thermistors) drives the pump. It converts electrical energy into mechanical energy, powering the hydraulic system.
2. Return Filter: This helps cleans the hydraulic fluid before it returns to the reservoir which helps Helps remove contaminants and prolongs the life of pumps, valves, and actuators.
3. Filler Breather: Keeps airborne dirt and moisture out when filling or when the fluid expands/contracts.
4. Level Indicator with Thermometer: Shows the oil level in the reservoir and provides a temperature reading (0–80°C range). Critical for monitoring system health — low fluid or overheating are early warning signs.
5. Relief Valve with Pressure Gauge: Protects the system from overpressure by diverting fluid when maximum pressure is reached.
6. Steel Tank (Reservoir): Stores hydraulic fluid and is coated with oil- and rust-proof paint for durability. Acts as both a storage unit and a heat sink, helping dissipate heat from the system.
7. Drain Port: To empty the reservoir during maintenance or oil changes.
What are the typical specifications (power range, flow rate, pressure) of industrial AC hydraulic power units?
Industrial AC hydraulic power units are designed for continuous, heavy-duty service, so their specifications are much broader than those of smaller DC or portable units. While exact figures depend on the application, most industrial HPUs fall within the following ranges:
Power: Industrial AC motors are typically 1.5 kW to 75 kW (4 HP to 100 HP), though very large systems can exceed 150 kW. Standard builds often use three-phase motors at 230V, 380V, or 460V for efficiency and reliability.
Flow Rate: Pump displacement and speed determine flow capacity. Industrial units usually deliver between 20 to 600 liters per minute (5 to 160 gallons per minute). High-volume systems, such as those in steel mills or offshore rigs, may go beyond 1,000 L/min.
Operating Pressure: Most units operate in the range of 100 to 350 bar (2,000 to 5,000 psi). Heavy-duty or specialized systems can be built for pressures above 420 bar (6,000 psi), depending on the pump design and safety requirements.
Reservoir Capacity: Reservoirs are sized to ensure proper cooling and fluid conditioning. Industrial tanks typically range from 11.5 litres to 2,500 litres, with larger custom designs available for continuous high-flow systems
What’s the importance of three-phase AC power in heavy-duty HPUs?
Single-phase AC power is fine for small, light-duty hydraulic setups, but three-phase AC power is essential for industrial HPUs that need high horsepower, reliability, and continuous operation.
| Feature | Single-Phase AC Power | Three-Phase AC Power |
|---|---|---|
| Motor Size | Typically up to ~5 HP | Commonly 5–100+ HP |
| Torque Delivery | Uneven, can cause vibration | Smooth, continuous torque |
| Start-up Ability | Struggles under heavy load | Starts easily under high load |
| Efficiency | Lower, higher current draw | Higher, lower current per phase |
| Applications | Light-duty, small machinery | Heavy-duty, continuous industrial systems |
| Availability | Residential & small workshops | Standard in industrial facilities |
What defines an industrial AC hydraulic power unit compared to mini AC power units?
An industrial AC hydraulic power unit is defined by its size, power capacity, and ability to operate continuously under heavy loads, while a mini AC power unit is built for compact, lower-demand applications.

Powering Heavy Industry with Confidence
From steel mills and foundries to offshore rigs and power plants, industrial AC hydraulic power units are the driving force behind some of the most demanding applications in the world. Their ability to deliver continuous power, handle extreme loads, and maintain reliability in harsh environments makes them indispensable to modern industry.
If you’re considering upgrading or specifying a hydraulic power unit for your operation, the choice often comes down to matching power, flow, and duty cycle to your application’s needs. Getting this right means more than just performance—it means long-term reliability, reduced downtime, and a safer workplace.
Looking for expert guidance on industrial AC hydraulic power units? Our team at Flowfit can help you size, design, and maintain the right solution for your industry. For more information, get in touch with our team of hydraulic specialists today.
The total one-stop supplier for hydraulic components & systems
Get in touch
Parys Road
Ludlow
Shropshire
SY8 1XY








